 Photo Source: https://phil.cdc.gov/Details.aspx?pid=7824 |
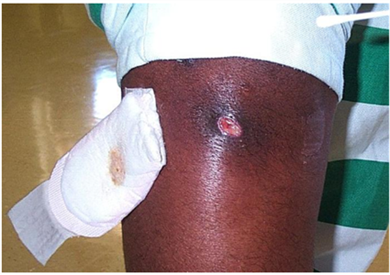
Staphylococcus aureus (“Staph”; S. aureus) is a bacteria commonly found on the skin and in the nose of healthy people. Staph can also be found in the armpit, groin, rectum or genital area, where it also can live without causing infection. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus, or MRSA, are Staph bacteria that have developed resistance to certain antibiotics (the beta-lactams) commonly used to treat Staph infections. |
Staph, including MRSA, can cause minor infections such as boils, or it can cause more serious infections, such as abscesses, pneumonia, bone, joint or bloodstream infections. Some MRSA skin infections are initially misdiagnosed as spider bites. However, verified spider bites are extremely rare and the spiders that cause significant bites are uncommon in Southern California. MRSA infections do not look different than those caused by other Staph aureus. More severe or potentially life-threatening MRSA infections occur most frequently among patients in healthcare settings. See Healthcare Associated Infections (HAIs) for more information.
S. aureus infections, including MRSA, are generally NOT reportable in Orange County, unless associated with an outbreak, or MRSA is identified in patient admitted to a healthcare facility. Outbreaks should be reported immediately by phone (714-834-8180) to OCHCA Epidemiology. Laboratory results from specimens from hospitals and skilled nursing facilities that are positive for MRSA meeting the criteria outlined in the Health Order Mandating reporting of MRSA, ESBLs, and CRE from Orange County hospitals and skilled nursing facilities should be reported to Orange County Epidemiology. Facilities should forward a list of results every 2 to 4 weeks, according to the process arranged by contacting OCHCA Epidemiology at 714-834-8180.
Healthcare Professionals
- Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of MRSA Infections in Adults and Children (Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) 2011)
- Outpatient Management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
- Factsheets for Clinicians
- MRSA in Healthcare Settings
Resources
- MRSA Factsheet
- Additional Factsheets & Posters for Parents and Athletes
- MRSA in the workplace
- A Parent’s Guide to MRSA in California
- Cleaning & Disinfection
Page Last Updated: 12/1/2023

